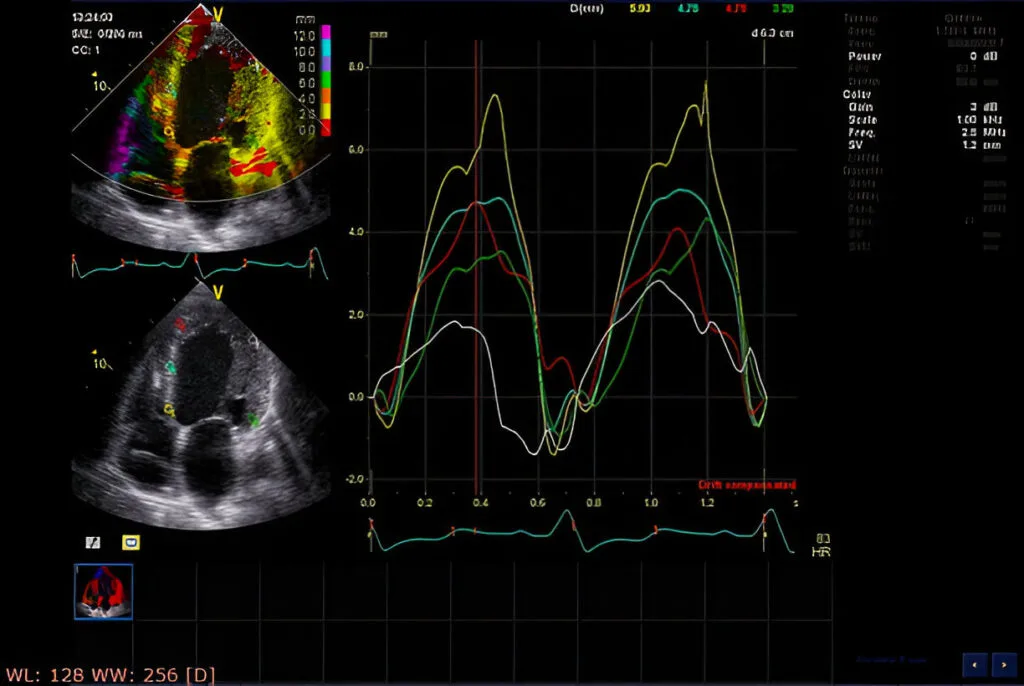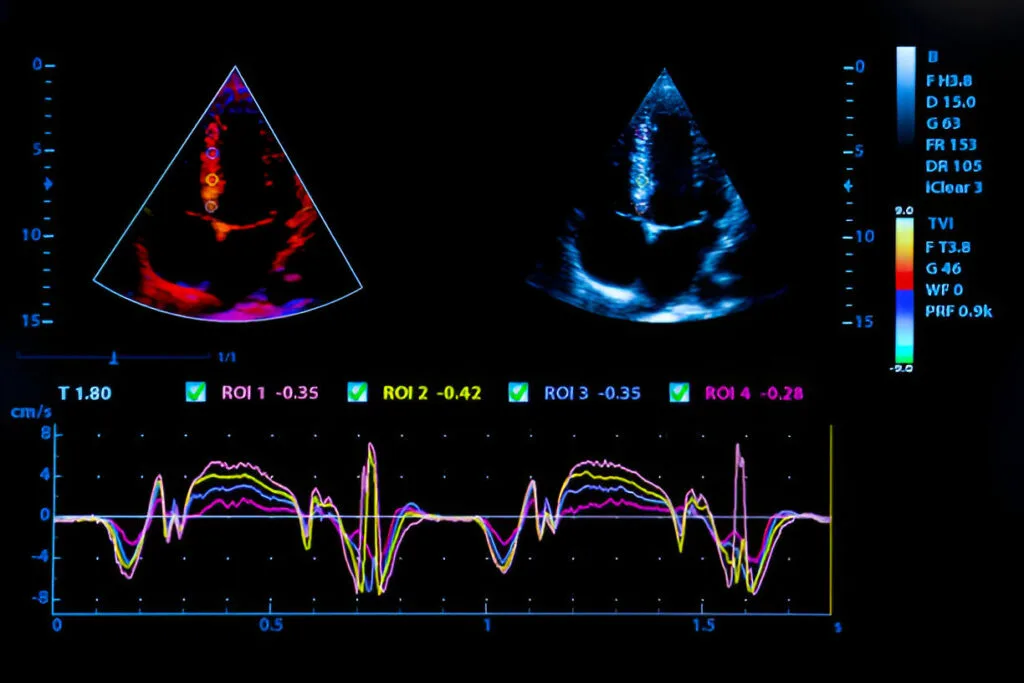
2D Echocardiography is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create real-time moving images of the heart. It allows doctors to examine the heart’s structure, function, and detect any abnormalities in its chambers and valves.
Heart Chambers and Walls: Assesses size, thickness, and motion of heart chambers and walls.
Valve Functionality: Detects narrowing (stenosis) or leakage (regurgitation) in heart valves.
Blood Flow: Evaluates blood flow through the heart and vessels to identify obstructions or irregularities.
Cardiac Function: Measures how efficiently the heart pumps blood.
Structural Abnormalities: Identifies congenital defects, tumors, or clots inside the heart.
Diagnosing and monitoring heart diseases like heart failure, cardiomyopathy, or valve disorders.
Detecting congenital heart defects.
Investigating symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath.
Pre-surgical assessment and post-surgical monitoring of cardiac patients.
The patient lies on an examination table, and a gel is applied to the chest.
A handheld device (transducer) is moved over the chest to capture heart images.
The test is painless, non-invasive, and usually takes 20–30 minutes.
2D echocardiography provides essential insights into the heart’s function and structure without invasive procedures. It enables early diagnosis, accurate treatment planning, and effective monitoring of heart conditions,